The Rise of Electric Vehicles: Driving Toward a Greener Future
In recent years, electric vehicles (EVs) have transitioned from niche novelties to mainstream contenders in the global automotive market. As concerns about climate change, air pollution, and fossil fuel dependence grow, EVs offer a compelling solution for a more sustainable future. But what exactly makes electric vehicles so appealing—and what challenges still lie ahead?
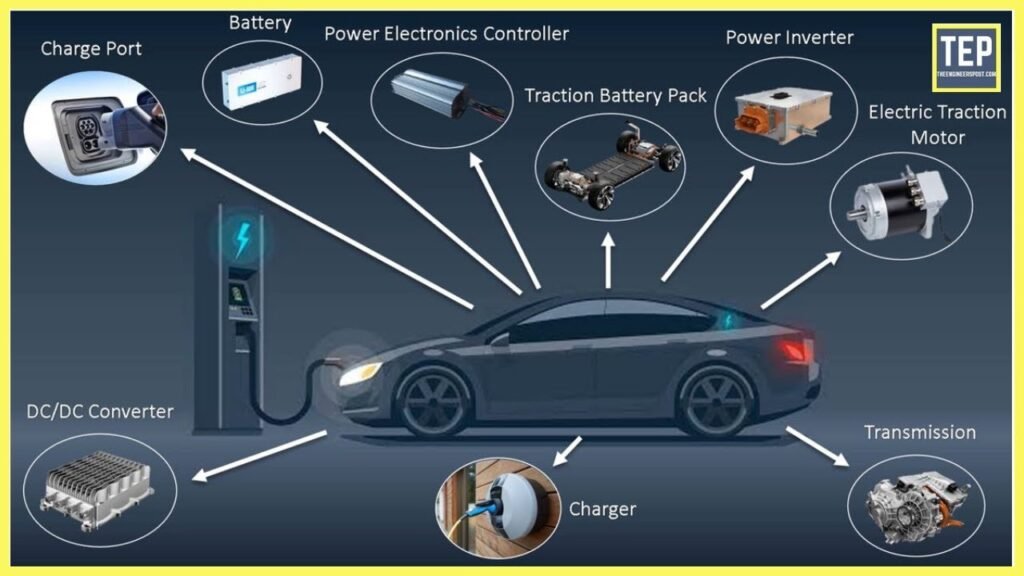
What Are Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles are cars powered entirely or partially by electricity. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that burn gasoline or diesel, EVs run on electric motors powered by batteries. The most common types of EVs include:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Fully electric, these vehicles rely solely on a rechargeable battery. Examples include the Tesla Model 3 and the Nissan Leaf.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These combine a battery-powered electric motor with a traditional engine. They can be charged via an outlet and also run on gasoline.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Powered by both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, but cannot be plugged in to recharge.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
- Environmental Impact
- Zero Emissions: BEVs produce no tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing greenhouse gases and air pollutants.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert over 77% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels—far more efficient than gasoline vehicles.
- Lower Operating Costs
- Fuel Savings: Electricity is typically cheaper than gasoline, especially when charging at home.
- Maintenance: Fewer moving parts mean fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs.
- Performance and Innovation
- EVs offer instant torque, making acceleration smooth and fast.
- Automakers are investing in smart technologies like autonomous driving, connected features, and over-the-air updates.

The Challenges Ahead
Despite the benefits, the EV revolution faces some hurdles:
- Charging Infrastructure: While expanding rapidly, public charging networks still lag in many regions, especially in rural areas.
- Battery Range and Cost: Although range is improving, concerns remain about long trips and battery replacement expenses.
- Supply Chain and Materials: The demand for lithium, cobalt, and other rare materials used in EV batteries raises ethical and environmental questions.
Government Support and Market Trends
Many governments around the world are encouraging the shift to EVs through incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and investment in charging infrastructure. Some countries and cities have even announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely within the next few decades.
The private sector is responding, too. Legacy automakers like Ford, GM, and Volkswagen are launching competitive EV models, while startups and tech companies are pushing innovation further.

Final Thoughts
Electric vehicles are more than just a trend—they’re a vital part of the global transition to clean energy. While challenges remain, advancements in technology and increasing public awareness are accelerating the shift. Whether you’re an eco-conscious driver, a tech enthusiast, or just someone looking to save money on gas, the future of driving is electric—and it’s already here.


